The Ultimate Film Crew Guide (Film Crew Positions)
When you’re starting out as a filmmaker, you’ll likely fill more than one role, especially when working with a smaller film crew. For smaller film productions, the number of film crew positions will vary with the budget. But if you want to work in any position on a larger film set, you'll need to understand the hierarchy of film crew positions and how the different departments work together during the production stages.
From directors, producers, and their assistants to more obscure crew members, our ultimate guide to film crew positions will give you an overview of a Hollywood-sized film production.
Boords is storyboarding software built for studios & agencies
Create consistent storyboards fast, iterate quickly, then share for feedback.
Try Boords FreeFilm production positions: an overview
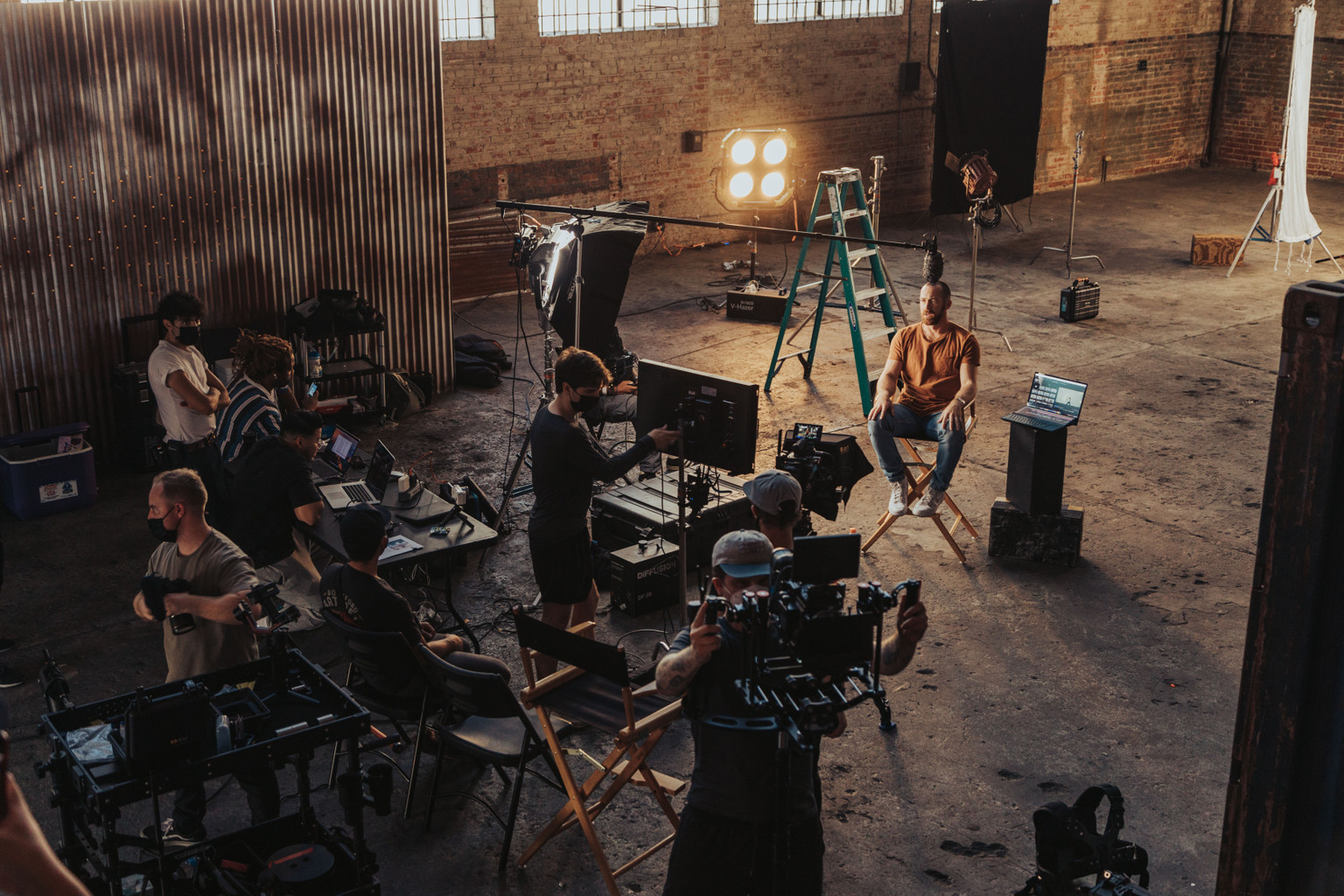
Filmmaking is a collaborative process during which many creative and technical roles work together to realize the director’s vision for a film. As a film industry rule of thumb, the size of the film crew and the total number of positions grow with the size of the film project.
The tasks and responsibilities of film crew members will vary as the production progresses, so who is doing the bulk of the work depends on the three distinct stages: pre-production, production or principal photography, and post-production. Film crew positions also fall into specific departments with a distinct hierarchy, ranging from department head to managers and down to assistants or interns.
Day-to-day tasks on a film set might have a more repetitive nature, especially when they have a strong technical or skill-based aspect, whereas, for other film crew positions, involvement can be more of a creative journey from inception to the finished project, or touch only a particular film production stage.
The stages of film production
The film production process follows the three sequential stages of pre-production, principal photography, and post-production. Important roles such as the director, art director, and production manager will have changing tasks and responsibilities over the three stages, while the involvement of other film production crew positions focuses on one particular stage only. Screenwriting is a development and pre-production job, for example, while an editor’s responsibilities fall into the post-production phase.
What are above-the-line and below-the-line film crew positions?
In a big Hollywood film production, a majority of the crew members are below-the-line personnel. What is the distinction between above and below the line? Anyone above the line is typically accounted for individually in the film’s budget: important leadership positions such as the director, screenwriter, cinematographer, art director, and producers will receive a negotiated compensation. The line producer will handle a large part of the production budget and the team below the line, production crew members who draw a daily or weekly salary for their tasks on the film set.
Film crew positions within the film production process
From the director’s vision to the final cut of a movie, how are the film crew positions distributed during the three production stages? Let’s look at the jobs during film production in sequence.
Pre-Production film crew positions
Production Management
Director: The director’s vision is guiding the production. Together with the screenwriter, they’ll finalize the shooting script and might be involved in creating storyboards together with the art department.
1st Assistant Director (1st AD): At this stage, they’ll prepare the shooting schedule.
Production Office
- Executive Producer: The role of an executive producer can differ. Occasionally they'll contribute in name only, but the executive producer can have a hand in financing the movie during pre-production or leverage film industry connections to attract talent and creatives or acquire intellectual property. The role is one of overseeing important production elements.
- Producer: A fundamental role, a producer is also a manager, for example, of funding, project steps and logistics, and other organizational tasks. The larger the production, the more individual producers will control specific aspects of the film production.
- Line Producer: Though this role will include many tasks, the line producer will concern themselves with planning and managing the budget and schedule during pre-production.
- Production Manager: With oversight of budget, scheduling, and staffing, the production manager reports to the line producer and supervises the production coordinator.
- Production Coordinator: They are in charge of coordinating logistics involving actors and actresses, film crew, and equipment.
- Production Assistant: As a common position to get started on a film set, these crew members take part in all aspects of production with a wide range of tasks.
Locations Department
- Location Manager: Their responsibility is to find shooting locations, as well as secure necessary permissions and adhere to laws and regulations for shooting on location.
- Location Scout: Working with the location manager, the location scout identifies and finds locations to realize the script. This includes dealing with the attached logistics and challenges.
Art Department
- Production Designer: As head of the art department, the production designer works closely with the director and cinematographer to realize the director's vision from the script, storyboards, and look-book to design, settings, and costumes.
- Art Director: Working under the production designer, the art director supervises the art department, often together with assistants. During pre-production, they're concerned with set creation and set dressing, and working on the look of the movie.
- Set: The Set Designer and Set Decorator plan and prepare sets, while the Set Dresser will furnish them. The smaller the production, the more these tasks will be concentrated in fewer roles, up to where the art director is also assuming the role of Set Designer. During pre-production, the Set Designer works on structures and interior spaces needed for film production.
Costumes & Wardrobe Department
- Costume Designer: The head of the wardrobe department, the Costume Designer, collaborates with the director during this production stage to create the clothing and look for costumes.
Production film crew positions during principal photography
Principal photography describes the production phase of a movie where the actual shooting takes place and film crew members work on the film set.
Production Management
- Director: Especially during the production stage, the director moves the project forward with great responsibility, authority, and influence over the entire film crew.
- First Assistant Director (1st AD): The 1st AD works at the side of the director to realize the director's vision, but their responsibilities also include the shooting schedule, running the set and film crew, and managing minute daily tasks. They're problem solvers.
- Second Assistant Director (2nd AD): Working below the 1st AD, the Second Assistant Director handles daily call sheets and makes sure talent appears at the set. They need a high-level understanding of how the other film departments operate and also distribute scripts to them.
- Visual & Special Effects Supervisor: Their responsibilities are the creative and technical aspects of visual and special effects, the practical and digital effects.
- Unit Production Manager: This administrative role oversees most issues and decisions regarding the budget and payroll.
- Set Production Assistant: The Set PA supports the needs of the shooting set and can be called upon to perform nearly any task.
Script Department / Continuity
- Script Supervisor: During principal photography, the Script Supervisor keeps track of the footage to make sure it follows the script and to match the continuity between shots.
Camera & Lighting Department
- Director of Photography (DP): As the head of the camera department, the director of photography creates and records the images following the director's vision using camera equipment, lighting, and framing. Cinematographer is another name for this role, and they also guide the grip and electrical department.
- First Assistant Camera (1st AC): The 1st AC handles camera equipment on set. A traditional name for this role is focus puller, as this was their primary task with analog photography. But with digital equipment, the 1st AC has to concern themselves with an array of image and camera settings.
- Second Assistant Camera (2nd AC): The second AC has the traditional task of operating the camera slate, but they're also in charge of gear, records, and help for the camera department.
- Camera Operator: When the DP or cinematographer doesn't control the camera themselves, they'll instruct a camera operator, especially during multi-camera shots.
- Digital Imaging Technician (DIT): This relatively new role on a film set stems from digital equipment. The DIT manages a digital image workflow. This is not a post-production role, but includes tasks of data management shortly after capture, ensuring the footage is up to par and fits the pre-defined looks for the production.
- Film Loader: This role is the analog equivalent of the DIT. They handle physical film before and after filming.
- Steadicam Operator: This specially trained camera operator handles a motion-stabilized camera rig.
- Gaffer: The Chief Lighting Technician or Gaffer is the head of the electric department and is responsible for the placement and powering of lights to fulfill the production's lighting plan. The Gaffer works closely with the DP.
- Best Boy or Best Babe: The BBE, Best Boy Electric or Best Babe Electric, is second to the Gaffer and delegates day-to-day electrical and lighting tasks, such as staffing and power supply.
- Electrician or Lighting Technician: Sets up and controls lighting equipment and electrical power on set.
Grips Department
- Key Grip: As the head of the grip department, the Key Grip collaborates with the Gaffer to control light, but also works on rigging, temporary structures, and physical support for other departments. Apart from their work on the lighting plan, the Key Grip will concern themselves with on-set safety.
- Best Boy Grip or Best Babe Grip: Second to the Key Grip, this role has managerial duties in the department in supporting the Key Grip.
- Grips: If anything needs moving on a film set, grips will move it. This can ensure not only safety but an organized and timely execution.
- Dolly Grip: This role handles the movement and placement of dollies, cranes and other heavy equipment needed for camera operation.
Sound Department
- Production Sound Mixer: This role records all sound during shooting day, as well as selecting and operating audio and mixing equipment.
- Boom Operator: Their classic role is to operate the boom mic, but they are also involved in placing other microphones around the set and achieving high-quality audio recordings.
- Sound Assistant: This "cable person" assists the sound department not only by laying cable but also by monitoring recording equipment and helping out.
Art Department
- Set Decorator: Their responsibility is to decorate the set during production, working with the Set Designer or the Art Director.
- Set Dresser: They specifically work on the shooting day's set, furniture, and design elements. On a smaller production, set design, dressing, and decoration might be rolled into one position, or be the responsibility of the Art Director.
- Props Master: They organize all props for the film project, except for weapons. A smaller production will have one role within the art department, whereas a Hollywood production can feature its own Props Department.
- Art Production Assistant: This role is a general art department assistant, though specialization, for example in set design, is possible.
Costumes & Wardrobe Department
- Costume Designer: As head of the Wardrobe Department, the Costume Designer collaborates with the director to ensure the proper look for all costumes.
- Costume Supervisor: Works with the costume designer to manage the on-set wardrobe. Formerly called wardrobe supervisor.
- Set Costumer: This role is an on-set representation of the wardrobe department to be on standby for adjustments as needed.
- Costume Coordinator: They keep track of everything to organize the Wardrobe Department.
- Tailor: They can alter or fix costumes on set as needed.
Hair & Makeup Department
- Makeup Artist: In charge of makeup and styling for the cast in line with the production design.
- Hairdresser: Responsible for hairstyles and upkeep.
Stunts Department
- Stunt Coordinator: They cast and supervise the stunt performers and design the on-set stunts, together with the director and cinematographer. They might use a choreographer for support.
- Stunt Performer: These professionals carry out the actual stunts.
Food Department
- Caterer and Craft: The Craft Service and Catering Department feed the crew and cast. Catering is for specific meals, whereas the Craft Service pertains to snacks, food, and drinks throughout the entire shooting day.
Get your FREE Filmmaking Storyboard Template Bundle
Plan your film with 10 professionally designed storyboard templates as ready-to-use PDFs.

Post-Production film crew positions
The final stage of the film production process after principal photography includes editing, as well as adding music, sound, and effects.
Editing Department
- Editor: They’re the creative head of the post-production process and work with the director to assemble and edit the footage.
Sound Department
- Sound Designer: In charge of post-production sound on a film, the sound designer selects and edits the on-set recordings to provide the editor with an audio track. Also called Supervising Sound Editor.
- Sound Editor: Assembles and edits all sound effects.
- Foley Artist: They create sound effects in sync with the final edit of a film.
- Composer: They write and perform the musical score for the final cut of the movie.
- Music Supervisor: They choose music separate from the original score for the film, and deal with licensing issues.
Visual Effects and Special Effects Department
- Visual Effects Editor: Together with the Visual Effects Supervisor, they add post-production visual effects.